BANKING DECISION ANALYTICS PROJECT
Banking in Emerging Economies
The determinants for the internationalization of banking are based on country characteristics and market dynamics and bank-specific advantages. Primarily the country characteristics consist of barriers to entry to provide services, the type of activities allowed and the type of investment allowed, as well as, regulations on capital flows and taxation and repatriation of profits, or indeed, tax benefits offered by a government to attract foreign banks to invest directly to encourage spill-over effects in the industry. The size of the market for banking products and specifically the product markets that are targeted and the potential growth of these are other factors. In terms of the foreign financial market dynamics the potential performance and profitability depends on the interaction and rivalry among existing banks in the market, the number of these their nationality and their size distribution, that is whether it a concentrated oligopolistic market with a few large banks and some other smaller banks, or it is a highly fragmented market. Different product markets and customer segments, that is, individual or corporate customers, may have different levels of rivalry and margins and hence profitability is different for each type. The more a bank has distinctive competencies the more that they may be transferred abroad. By definition when they have distinctive there must be some competitive advantage for the bank. The decision to enter an emerging economy by a multinational bank is a very important one, as many factors need to be considered. You are required to consider the following Raw Banking Data with 280 factors and thr following 24 countries in four continents for this project.
- Algeria
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- China
- Czech Republic
- Estonia
- Georgia
- Hungary
- India
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Mexic
- Morocco
- Poland
- Romania
- Russia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Vietnam
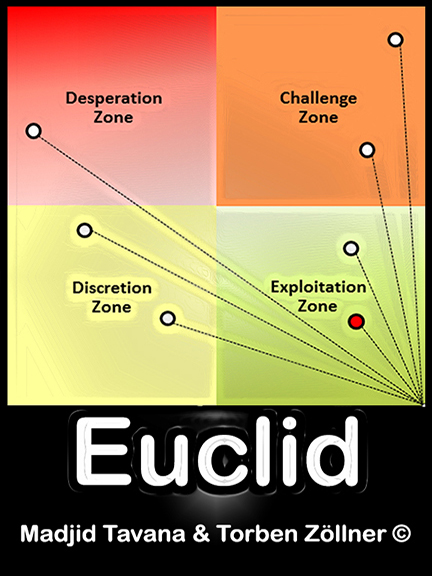
You are required to consider the following (Raw Banking Data) with 280 factors and 24 countries in four continents for this project. Organize your 280 factors into opportunities (strengths) and threats (weaknesses) reasonably or by using Internet resources for questionable factors. Also, clean up the data and watch for duplicates. You are then required to do all necessary calculations in excel for the Euclid model. Your Euclid model and the CSV file used in the Euclid program must produce similar results. While the Euclid numbers are precise, you may experience up to ± 0.02 rounding differences in the average opportunity and the average threat scores between Excel and Euclid due to Excel rounding. This may also result in a small variation among the final rankings of the countries in Excel and Euclid. The Excel file must include a complete scatter chart for the Euclid model. This includes all data labels, ideal point, nadir point, coordinates, average partition lines, and the four quadrants. The spreadsheet must also include the Euclidean distances and rankings with reference to the ideal point. All formulas must be preserved in the spreadsheet. Finally, your spreadsheet must include a radar chart and a world heatmap of the Euclidean distances for the 24 countries considered in your study. Please refer to Get started with 3D Maps (maps.pdf) for this requirement.
Additional Resources:
Useful Links:
NationMaster - World Statistics
World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency
Library of Congress - Country Studies
World Bank - World Development Indicators
Transparency International
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development: Better Life IndexDecision Models:
Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) (Problem)
MCDM (Solutions)
André and Angelique: Buying Their Dream Home (Problem)
Problem
CSV File
André and Angelique: Buying Their Dream Home (Solution)
Solution
McDonald’s Corporation Location Planning (Problem)
Problem
Labeling Points on a Euclid Scatter Chart
Fixing the #VALUE! Error Messages in your Euclid Spreadsheet
Get started with Excel 3D Maps
Useful Papers:
- Tavana, M. (2008) 'Fahrenheit 59: An Environmental Decision Support System for Benchmarking Global Warming at Johnson Space Center
,' Benchmarking: An International Journal, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 307-325.
- Tavana, M., Bourgeois, B.S. and Sodenkamp, M. (2009) 'Fuzzy Multiple Criteria Base Realignment and Closure (BRAC) Benchmarking System at the Department of Defense

,' Benchmarking: An International Journal, Vol. 16, No. 2, pp. 192-221.
- Tavana, M. and O’Connor, A. (2010) 'An Integrated Strategic Benchmarking Model for Assessing International Alliances with Application to NATO Membership Enlargement

,' Benchmarking: An International Journal, Vol. 17, No. 6, pp. 791-806.
- Tavana, M., Sodenkamp, M. and Suhl, L. (2010) 'A Soft Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Model with Application to the European Union Enlargement

,' Annals of Operations Research, Vol. 181, No. 1, pp. 393-421.
- Tavana, M., Di Caprio, D., Santos-Arteaga, F.J. and O'Connor, A. (2015) 'A Novel Entropy-Based Decision Support Framework for Uncertainty Resolution in the Initial Subjective Evaluations of Experts: The NATO Enlargement Problem

,' Decision Support Systems, Vol. 74, pp. 135-149.
Final Report Outline:
- Cover Page
- Executive Summary
- Introduction and Problem description
- Proposed method (include step-by-step description)
- Results (include Euclidean distance and overall rankings, scatter chart with four quadrants, radar chart, world heath map, etc.)
- Recommendations and conclusions
- References
- Appendices
Sample Consulting Reports:
Final Report Submission:
Submit your WORD, EXCEL, and CSV files via the following E-mail: tavanadropbox@gmail.com